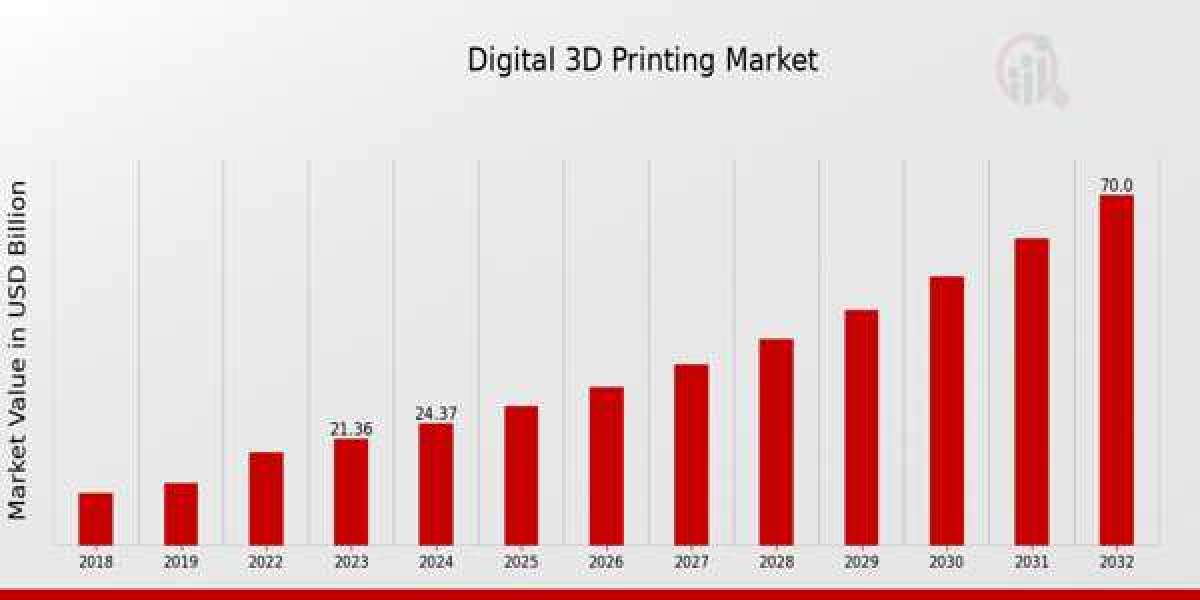
Digital 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a transformative technology that builds three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital design. Here's a breakdown of key aspects:
Core Concepts:
- Additive Process:
- Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing (e.g., machining), 3D printing adds material to create an object.
- This layer-by-layer construction allows for complex geometries and intricate designs.
- Digital Design:
- The process begins with a digital 3D model, typically created using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- Material Variety:
- 3D printing utilizes a wide range of materials, including:
- Plastics (various types)
- Metals (titanium, steel, aluminum)
- Resins
- Ceramics
- Composites
- even biological materials.
- 3D printing utilizes a wide range of materials, including:
Key 3D Printing Technologies:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM):
- Extrudes thermoplastic filament layer by layer.
- Widely used for prototyping and hobbyist applications.
- Stereolithography (SLA):
- Uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid layers.
- Produces high-resolution parts with smooth surfaces.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS):
- Uses a laser to fuse powdered materials (e.g., nylon, metal) into solid layers.
- Suitable for functional prototypes and end-use parts.
- Material Jetting:
- deposits droplets of photopolymer resin, that are then cured by UV light.
- Binder Jetting:
- applies a liquid binding agent to join powder materials.
Applications:
- Prototyping: Rapidly creating physical prototypes for design validation.
- Manufacturing: Producing custom parts, tools, and end-use products.
- Healthcare: Creating medical implants, prosthetics, and surgical guides.
- Aerospace: Manufacturing lightweight and complex aircraft components.
- Automotive: Producing custom parts and tooling.
- Construction: 3D printing building components and even entire structures.
- Consumer Products: Creating personalized items and custom designs.
Trends:
- Advanced Materials: Ongoing research and development of new 3D printing materials with enhanced properties.
- Increased Automation: Integration of robotics and automation to improve efficiency and scalability.
- Metal 3D Printing: Growing adoption of metal 3D printing for industrial applications.
- Bioprinting: 3D printing of biological tissues and organs.
3D printing continues to revolutionize various industries, offering greater design freedom, faster production times, and the ability to create highly customized products.